Supervised Machine Leaning
Introduction
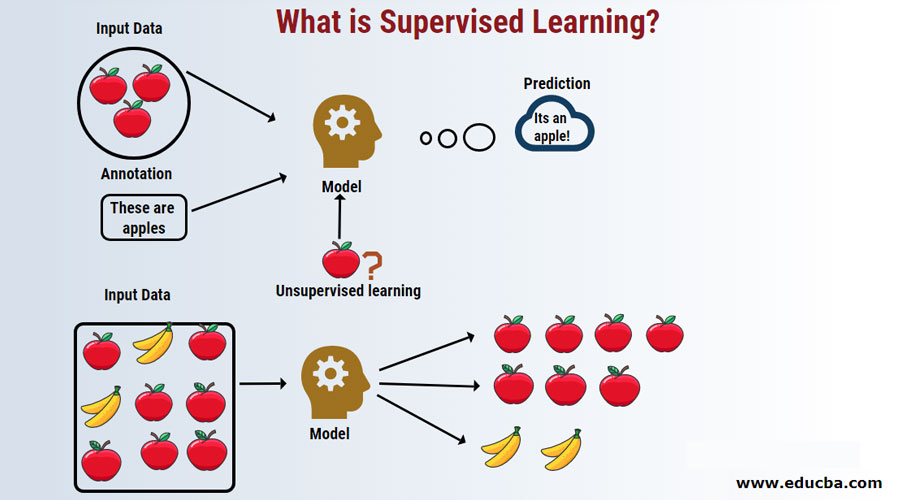
Supervised learning is a type of machine learning where the algorithm learns from labeled data, meaning each example in the dataset is paired with a corresponding output label or target. The goal of supervised learning is to learn a mapping function from input data to output labels, so that when given new input data, the algorithm can predict or classify the correct output label.
Here's how supervised learning works:
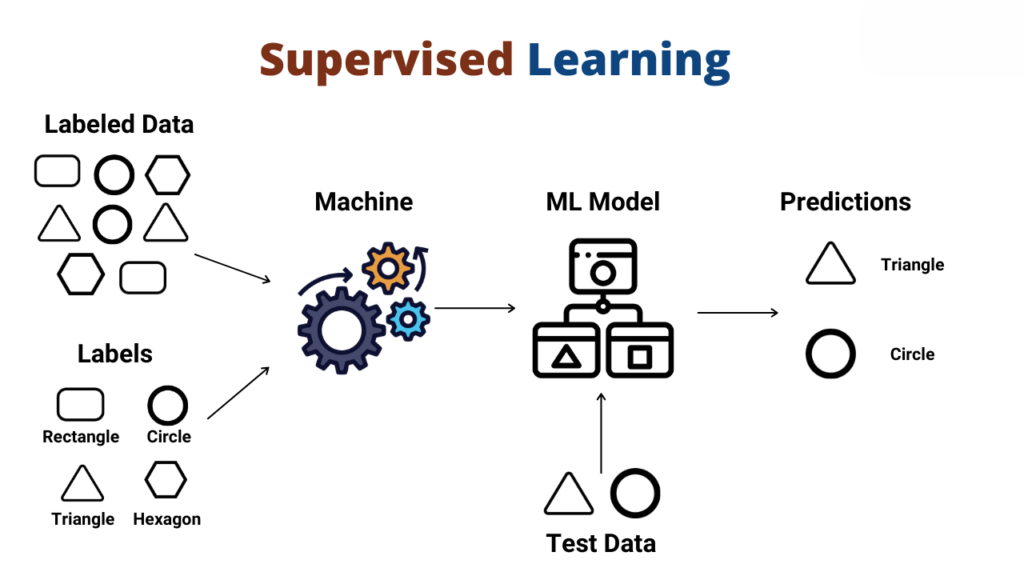
- Labeled Data: The training dataset used in supervised learning consists of examples where each input data point is associated with a known output label. These labels are provided by humans or generated through manual annotation.
- Training Process: During the training process, the algorithm learns to identify patterns and relationships between the input features and the output labels by iteratively adjusting its internal parameters. The objective is to minimize the difference between the predicted output and the true output labels in the training data.
- Model Representation: The learned mapping function is typically represented by a mathematical model, such as a decision tree, support vector machine, logistic regression, or neural network, depending on the complexity of the problem and the nature of the data.
- Predict: Once the model is trained, it can be used to make predictions or classifications on new, unseen input data. The algorithm applies the learned mapping function to the new data to generate predictions or classifications based on the patterns it learned during training.
- Evaluation: The performance of the supervised learning model is evaluated using a separate validation or test dataset that was not used during training. This evaluation helps assess the model's ability to generalize to new, unseen data and provides insights into its accuracy and effectiveness.
Supervised learning tasks can be broadly categorized into two main types:
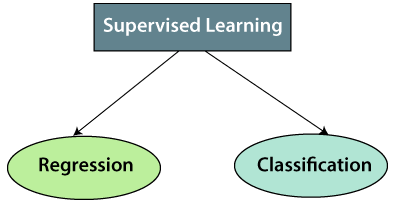
- Classification: In classification tasks, the output variable is categorical, meaning it belongs to a finite set of classes or categories. The goal is to assign a class label to each input data point. Examples include email spam detection, sentiment analysis, and image classification.
- Regression: In regression tasks, the output variable is continuous, meaning it can take on any numerical value within a range. The goal is to predict a continuous value or quantity based on the input features. Examples include predicting house prices, estimating sales revenue, and forecasting stock prices.
Supervised learning is widely used in various applications across industries, including healthcare, finance, marketing, and natural language processing, among others. It is a powerful approach for solving predictive modeling problems where labeled data is available for training.